Every time you send a message, watch a video or browse the web, you are relying on a vast network of underwater cables that span continents and support the digital world. The seamless communication and connectivity we often take for granted are made possible by these undersea cables also known as submarine cables, which discreetly transport 99 percent of the world’s internet traffic along the ocean floor. But how are these cables laid? How do they function under the immense pressure of deep water? Moreover, why are they essential for our digital future?
The article will explore the fascinating process of installing undersea cables, revealing the underlying technologies and the vital role these submarine cables play in global connectivity. Be ready to learn how these cables improve our digital experience and enable us to stay connected at any distance. This is the unsung tale of the internet’s underwater journey.
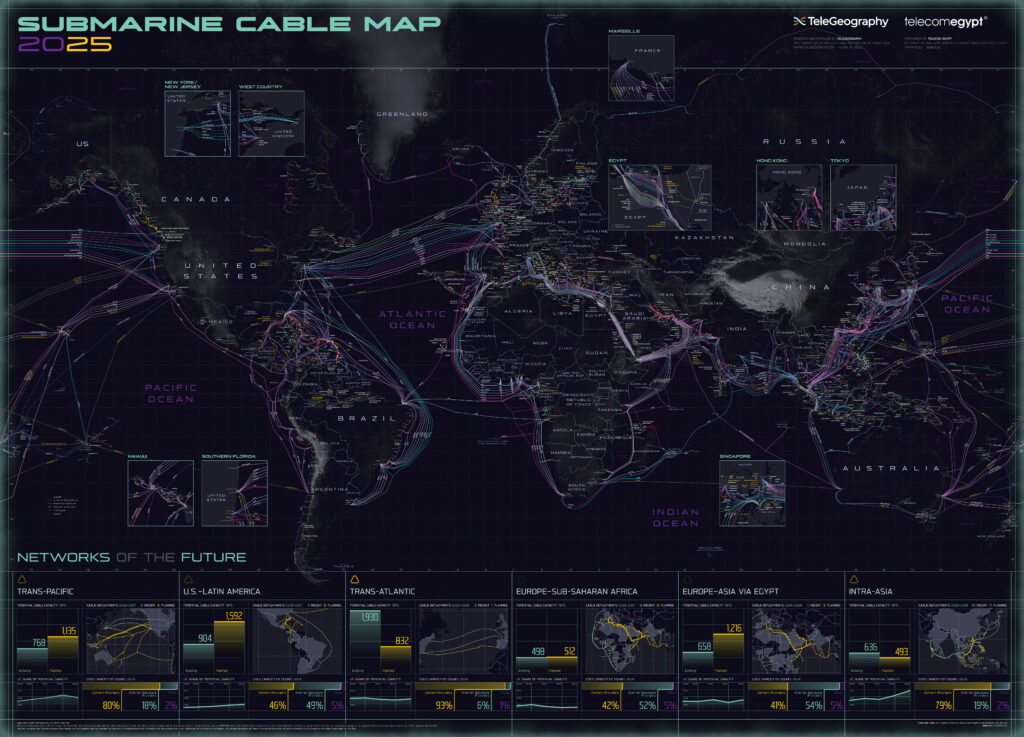
Click on the link to view Global Submarine Cable Map 2025
SUBMARINE CABLE MAP 2025